dubbo是如何控制并发数和限流的?
- Dubbo
- 时间:2021-08-20 09:00
- 6585人已阅读
简介
ExecuteLimitFilterExecuteLimitFilter,在服务提供者,通过的"executes"统一配置项开启:表示每服务的每方法最大可并行执行请求数。ExecuteLimitFilter是通过信号量来实现的对服务端的并发数的控制。ExecuteLimitFilter执行流程:1:首先会去获得服务提供者每服务每方法最大可并行执行请求数2:如果每服务每方法最大可
🔔🔔🔔好消息!好消息!🔔🔔🔔
有需要的朋友👉:联系凯哥
ExecuteLimitFilter
1:首先会去获得服务提供者每服务每方法最大可并行执行请求数
2:如果每服务每方法最大可并行执行请求数大于零,那么就基于基于服务 URL + 方法维度获取一个RpcStatus实例
3:通过RpcStatus实例获取一个信号量,若果获取的这个信号量调用tryAcquire返回false,则抛出异常
4:如果没有抛异常,那么久调用RpcStatus静态方法beginCount,给这个 URL + 方法维度开始计数
5:调用服务
6:调用结束后计数调用RpcStatus静态方法endCount,计数结束
7:释放信号量
ExecuteLimitFilter源码如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
Semaphore executesLimit = null;
boolean acquireResult = false;
int max = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.EXECUTES_KEY, 0);
if (max > 0) {
RpcStatus count = RpcStatus.getStatus(url, invocation.getMethodName());
// if (count.getActive() >= max) {
/**
* http://manzhizhen.iteye.com/blog/2386408
* use semaphore for concurrency control (to limit thread number)
*/
executesLimit = count.getSemaphore(max);
if(executesLimit != null && !(acquireResult = executesLimit.tryAcquire())) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " in provider " + url + ", cause: The service using threads greater than <dubbo:service executes=\"" + max + "\" /> limited.");
}
}
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean isSuccess = true;
RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
isSuccess = false;
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new RpcException("unexpected exception when ExecuteLimitFilter", t);
}
} finally {
RpcStatus.endCount(url, methodName, System.currentTimeMillis() - begin, isSuccess);
if(acquireResult) {
executesLimit.release();
}
}
} private static final ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, RpcStatus>> METHOD_STATISTICS = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, RpcStatus>>();
public static RpcStatus getStatus(URL url, String methodName) {
String uri = url.toIdentityString();
ConcurrentMap<String, RpcStatus> map = METHOD_STATISTICS.get(uri);
if (map == null) {
METHOD_STATISTICS.putIfAbsent(uri, new ConcurrentHashMap<String, RpcStatus>());
map = METHOD_STATISTICS.get(uri);
}
RpcStatus status = map.get(methodName);
if (status == null) {
map.putIfAbsent(methodName, new RpcStatus());
status = map.get(methodName);
}
return status;
} private volatile int executesPermits;
public Semaphore getSemaphore(int maxThreadNum) {
if(maxThreadNum <= 0) {
return null;
}
if (executesLimit == null || executesPermits != maxThreadNum) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executesLimit == null || executesPermits != maxThreadNum) {
executesLimit = new Semaphore(maxThreadNum);
executesPermits = maxThreadNum;
}
}
}
return executesLimit;
}TPSLimiter
1:通过 配置项,添加到 或 或 中开启,例如:
dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoServiceImpl" protocol="injvm" > <dubbo:parameter key="tps" value="100" /> </dubbo:service>
通过 配置项,设置 TPS 周期。
源码分析
private final TPSLimiter tpsLimiter = new DefaultTPSLimiter();
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (!tpsLimiter.isAllowable(invoker.getUrl(), invocation)) {
throw new RpcException(
"Failed to invoke service " +
invoker.getInterface().getName() +
"." +
invocation.getMethodName() +
" because exceed max service tps.");
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} private final ConcurrentMap<String, StatItem> stats
= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, StatItem>();
@Override
public boolean isAllowable(URL url, Invocation invocation) {
//获取tps这个参数设置的大小
int rate = url.getParameter(Constants.TPS_LIMIT_RATE_KEY, -1);
//获取tps.interval这个参数设置的大小,默认60秒
long interval = url.getParameter(Constants.TPS_LIMIT_INTERVAL_KEY,
Constants.DEFAULT_TPS_LIMIT_INTERVAL);
String serviceKey = url.getServiceKey();
if (rate > 0) {
StatItem statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
if (statItem == null) {
stats.putIfAbsent(serviceKey,
new StatItem(serviceKey, rate, interval));
statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
}
return statItem.isAllowable();
} else {
StatItem statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
if (statItem != null) {
stats.remove(serviceKey);
}
}
return true;
} private long lastResetTime;
private long interval;
private AtomicInteger token;
private int rate;
public boolean isAllowable() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 若到达下一个周期,恢复可用种子数,设置最后重置时间。
if (now > lastResetTime + interval) {
token.set(rate);// 回复可用种子数
lastResetTime = now;// 最后重置时间
}
// CAS ,直到或得到一个种子,或者没有足够种子
int value = token.get();
boolean flag = false;
while (value > 0 && !flag) {
flag = token.compareAndSet(value, value - 1);
value = token.get();
}
return flag;
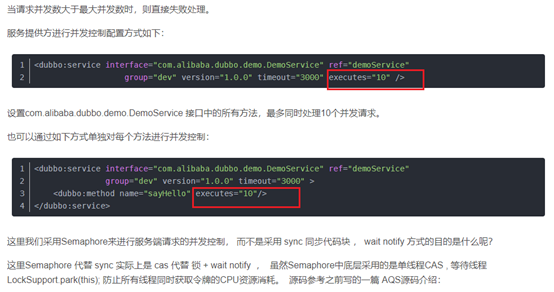
}dubbo 并发控制 和 连接控制
并发控制
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" executes="10" />
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService"> <dubbo:method name="sayHello" executes="10" /> </dubbo:service>
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" actives="10" />
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" loadbalance="leastactive" />
连接控制
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" connections="10" />
下一篇: 项目中常用的19条MySQL优化技巧